 Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are to electronic devices what a cornerstone is to a building. PCBs are the foundational building blocks that all other materials are referenced to in assembling an electronic device. A better understanding of the everyday devices build upon PCPs helps identify their importance.
Printed circuit boards (PCBs) are to electronic devices what a cornerstone is to a building. PCBs are the foundational building blocks that all other materials are referenced to in assembling an electronic device. A better understanding of the everyday devices build upon PCPs helps identify their importance.
What Are PCBs?
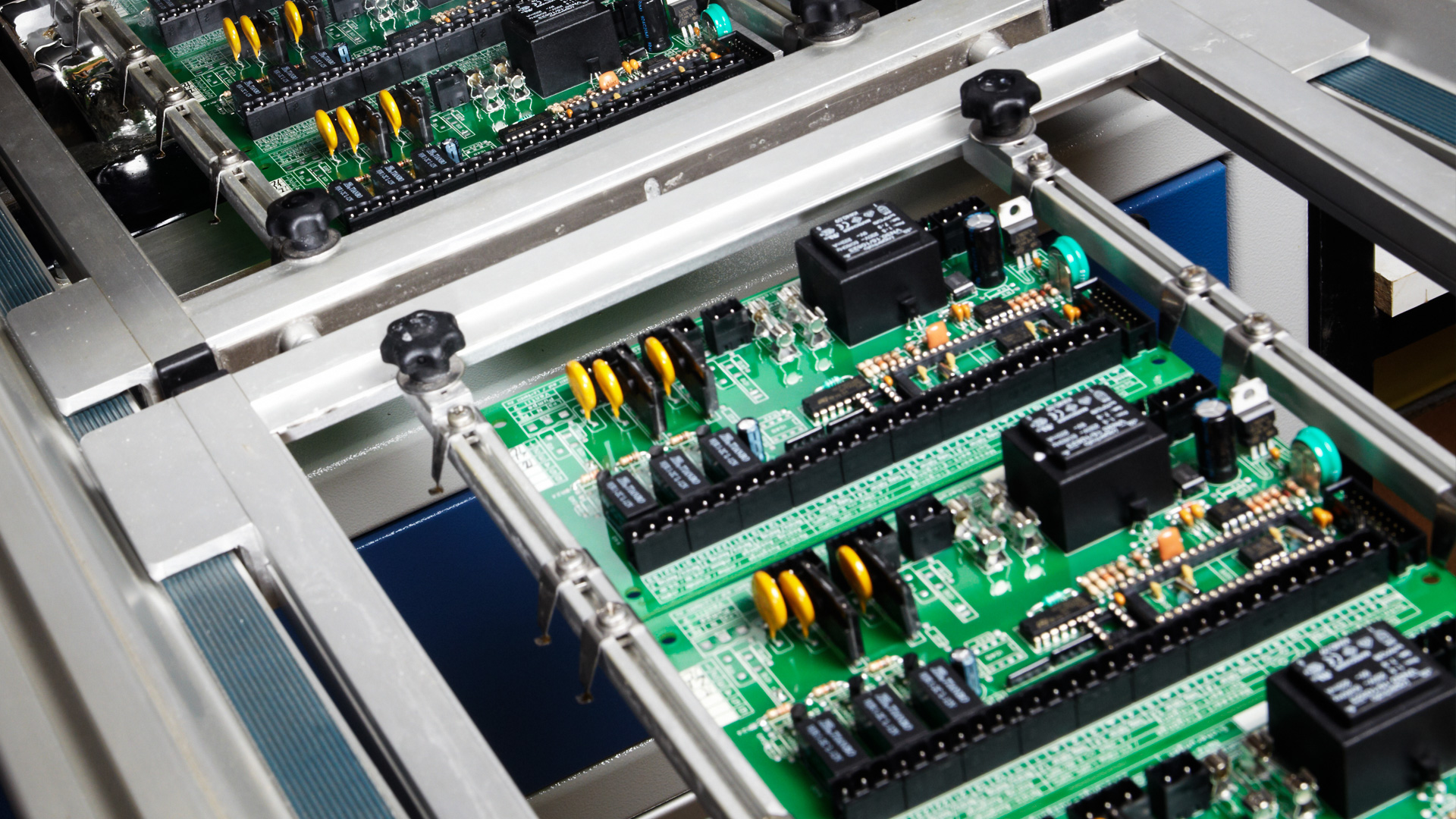
PCBs are made of electrical components and connectors linked together by conductive circuits that are usually made of copper. Routing power and electrical signals within and between devices is the purpose of PCBs. First developed in the early 20th century, PCBs have undergone rapid development as technology advanced, and their use became widespread. The development of electronic circuit design in San Jose continues to occur as the industry seeks to produce smaller and more efficient electronic devices.
Where Are PCBs Used?
Because they are small and lightweight, PCB’s are used in many modern devices and complex systems. The medical field uses them in imaging systems, radiation equipment, computers, and MRI machines as well as pacemakers, implantable devices, hearing aids, and miniature cameras used in minimally invasive procedures. Innovation continues to occur medical PCB design field.
The aerospace industry uses PCBs for many of the same reasons in dashboards, flight controls, safety systems, instrument panels, and flight management systems. They work in applications where high vibrations occur like flying in a rocket to Mars and are lightweight, resulting in less lower fuel requirements. Equipment exposed to shock, heavy impact, and vibrations like military vehicles, modern weapons, electronic systems, and ruggedized computers are another application for PCBs.
Garage door openers are made with a simple single PCB, smartwatches are made with six PCBs, and supercomputers and servers are made with 60 PCBs. Simple devices many people use every day like garage door openers, and smartwatches would not be the same without PCBs, and neither would supercomputers like those used for rocket launches and space exploration.

